Free Access
| Issue |
ESAIM: M2AN
Volume 40, Number 4, July-August 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 785 - 814 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/m2an:2006030 | |
| Published online | 15 November 2006 | |
- R. Akhavan and Q. Zhou, A comparison of FENE and FENE-P dumbbell and chain models in turbulent flow. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 109 (2003) 115–155. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- N. Arada and A. Sequeira, Strong steady solutions for a generalized Oldroyd-B model with shear-dependent viscosity in a bounded domain. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. S. 13 (2003) 1303–1323. [Google Scholar]
- F.P.T. Baaijens, Mixed finite element methods for viscoelastic flow analysis: a review. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 79 (1998) 361–385. [Google Scholar]
- I. Babuška, R. Durán and R. Rodríguez, Analysis of the efficiency of an a posteriori error estimator for linear triangular finite elements. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29 (1992) 947–964. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- J. Baranger and H. El Amri, Estimateurs a posteriori d'erreur pour le calcul adaptatif d'écoulements quasi-newtoniens. RAIRO Modél. Math. Anal. Numér. 25 (1991) 931–947. [Google Scholar]
- J. Baranger and D. Sandri, Finite element approximation of viscoelastic fluid flow: existence of approximate solutions and error bounds. I. Discontinuous constraints. Numer. Math. 63 (1992) 13–27. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- J. Baranger and S. Wardi, Numerical analysis of a FEM for a transient viscoelastic flow. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 125 (1995) 171–185. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- J.W. Barrett, C. Schwab and E. Süli, Existence of global weak solutions for some polymeric flow models. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. S. 15 (2005) 939–983. [Google Scholar]
- R. Bird, C. Curtiss, R. Armstrong and O. Hassager, Dynamics of polymeric liquids, Vol. 1 and 2. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- A. Bonito, Ph. Clément and M. Picasso, Mathematical and numerical analysis of a simplified time-dependent viscoelastic flow. Numer. Math. (submitted). [Google Scholar]
- A. Bonito, Ph. Clément and M. Picasso, Mathematical analysis of a simplified Hookean dumbbells model arising from viscoelastic flows. J. Evol. Equ. 6 (2006) 381–398. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- A. Bonito, M. Picasso and M. Laso, Numerical simulation of 3d viscoelastic flows with complex free surfaces. J. Comput. Phys. 215 (2006) 691–716. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- J. Bonvin and M. Picasso, Variance reduction methods for connffessit-like simulations. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 84 (1999) 191–215. [Google Scholar]
- J. Bonvin and M. Picasso, A finite element/Monte-Carlo method for polymer dilute solutions. Comput. Vis. Sci. 4 (2001) 93–98. Second AMIF International Conference (Il Ciocco, 2000). [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- J. Bonvin, M. Picasso and R. Stenberg, GLS and EVSS methods for a three-field Stokes problem arising from viscoelastic flows. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 190 (2001) 3893–3914. [Google Scholar]
- B.H.A.A. van den Brule, A.P.G. van Heel and M.A. Hulsen, Simulation of viscoelastic flows using Brownian configuration fields. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 70 (1997) 79–101. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B.H.A.A. van den Brule, A.P.G. van Heel and M.A. Hulsen, On the selection of parameters in the FENE-P model. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 75 (1998) 253–271. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B.H.A.A van den Brule, M.A. Hulsen and H.C. Öttinger, Brownian configuration fields and variance reduced connffessit. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 70 (1997) 255–261. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B. Buffoni and J. Toland, Analytic theory of global bifurcation. Princeton Series in Applied Mathematics. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, (2003). [Google Scholar]
- G. Caloz and J. Rappaz, Numerical analysis for nonlinear and bifurcation problems, in Handbook of numerical analysis, Vol. V, North-Holland, Amsterdam (1997) 487–637. [Google Scholar]
- C. Chauvière and A. Lozinski, A fast solver for Fokker-Planck equation applied to viscoelastic flows calculations: 2D FENE model. J. Comput. Phys. 189 (2003) 607–625. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- P.G. Ciarlet and J.-L. Lions, editors, Handbook of numerical analysis. Vol. II. North-Holland, Amsterdam, (1991). Finite element methods. Part 1. [Google Scholar]
- P. Clément, Approximation by finite element functions using local regularization. RAIRO Anal. Numér. 9 (1975) 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- G. Da Prato and J. Zabczyk, Stochastic equations in infinite dimensions, Vol. 44 of Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1992). [Google Scholar]
- W. E, T. Li and P. Zhang, Convergence of a stochastic method for the modeling of polymeric fluids. Acta Math. Sin. 18 (2002) 529–536. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- W. E, T. Li and P. Zhang, Well-posedness for the dumbbell model of polymeric fluids. Comm. Math. Phys. 248 (2004) 409–427. [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- V.J. Ervin and N. Heuer, Approximation of time-dependent, viscoelastic fluid flow: Crank-Nicolson, finite element approximation. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 20 (2004) 248–283. [Google Scholar]
- V.J. Ervin and W.W. Miles, Approximation of time-dependent viscoelastic fluid flow: SUPG approximation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41 (2003) 457–486 (electronic). [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- X. Fan, Molecular models and flow calculation: I. the numerical solutions to multibead-rod models in inhomogeneous flows. Acta Mech. Sin. 5 (1989) 49–59. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- X. Fan, Molecular models and flow calculation: II. simulation of steady planar flow. Acta Mech. Sin. 5 (1989) 216–226. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M. Farhloul and A.M. Zine, A new mixed finite element method for viscoelastic fluid flows. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 7 (2003) 93–115. [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- E. Fernández-Cara, F. Guillén and R.R. Ortega, Mathematical modeling and analysis of viscoelastic fluids of the Oldroyd kind, in Handbook of numerical analysis, Vol. VIII, North-Holland, Amsterdam (2002) 543–661. [Google Scholar]
- A. Fortin, R. Guénette and R. Pierre, On the discrete EVSS method. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 189 (2000) 121–139. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M. Fortin and R. Pierre, On the convergence of the mixed method of Crochet and Marchal for viscoelastic flows. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 73 (1989) 341–350. [Google Scholar]
-
Y. Giga, Analyticity of the semigroup generated by the Stokes operator in
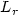 spaces. Math. Z. 178 (1981) 297–329.
[CrossRef]
[MathSciNet]
[Google Scholar]
spaces. Math. Z. 178 (1981) 297–329.
[CrossRef]
[MathSciNet]
[Google Scholar]
- E. Grande, M. Laso and M. Picasso, Calculation of variable-topology free surface flows using CONNFFESSIT. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 113 (2003) 127–145. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- C. Guillopé and J.-C. Saut, Existence results for the flow of viscoelastic fluids with a differential constitutive law. Nonlinear Anal-theor. 15 (1990) 849–869. [Google Scholar]
- B. Jourdain, T. Lelièvre and C. Le Bris, Numerical analysis of micro-macro simulations of polymeric fluid flows: a simple case. Math. Mod. Meth. Appl. S. 12 (2002) 1205–1243. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B. Jourdain, C. Le Bris and T. Lelièvre, On a variance reduction technique for micro-macro simulations of polymeric fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 122 (2004) 91–106. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B. Jourdain, T. Lelièvre and C. Le Bris, Existence of solution for a micro-macro model of polymeric fluid: the FENE model. J. Funct. Anal. 209 (2004) 162–193. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- B. Jourdain, C. Le Bris, T. Lelièvre and F. Otto, Long-time asymptotics of a multiscale model for polymeric fluid flows. Arch. Ration. Mech. An. 181 (2006) 97–148. [Google Scholar]
- I. Karatzas and S.E. Shreve, Brownian motion and stochastic calculus, volume 113 of Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Springer-Verlag, New York (1991). [Google Scholar]
- R. Keunings, On the Peterlin approximation for finitely extensible dumbbells. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 68 (1997) 85–100. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- R. Keunings, Micro-marco methods for the multi-scale simulation of viscoelastic flow using molecular models of kinetic theory, in Rheology Reviews, D.M. Binding, K. Walters (Eds.), British Society of Rheology (2004) 67–98. [Google Scholar]
- S. Larsson, V. Thomée and L.B. Wahlbin, Numerical solution of parabolic integro-differential equations by the discontinuous Galerkin method. Math. Comp. 67 (1998) 45–71. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- M. Laso and H.C. Öttinger, Calculation of viscoelastic flow using molecular models: the connffessit approach. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 47 (1993) 1–20. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M. Laso, H.C. Öttinger and M. Picasso, 2-d time-dependent viscoelastic flow calculations using connffessit. AICHE Journal 43 (1997) 877–892. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- C. Le Bris and P.-L. Lions, Renormalized solutions of some transport equations with partially W1,1 velocities and applications. Ann. Mat. Pur. Appl. 183 (2004) 97–130. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- T. Lelièvre, Optimal error estimate for the CONNFFESSIT approach in a simple case. Comput. Fluids 33 (2004) 815–820. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- T. Li and P. Zhang, Convergence analysis of BCF method for Hookean dumbbell model with finite difference scheme. Multiscale Model. Simul. 5 (2006) 205–234. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- T. Li, H. Zhang and P. Zhang, Local existence for the dumbbell model of polymeric fluids. Comm. Partial Diff. Eq. 29 (2004) 903–923. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- P.L. Lions and N. Masmoudi, Global solutions for some Oldroyd models of non-Newtonian flows. Chinese Ann. Math. Ser. B 21 (2000) 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- A. Lozinski and R.G. Owens, An energy estimate for the Oldroyd B model: theory and applications. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 112 (2003) 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- A. Lunardi, Analytic semigroups and optimal regularity in parabolic problems. Progress in Nonlinear Differential Equations and their Applications, 16 Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel (1995). [Google Scholar]
- A. Machmoum and D. Esselaoui, Finite element approximation of viscoelastic fluid flow using characteristics method. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 190 (2001) 5603–5618. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- K. Najib and D. Sandri, On a decoupled algorithm for solving a finite element problem for the approximation of viscoelastic fluid flow. Numer. Math. 72 (1995) 223–238. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- H.C. Öttinger, Stochastic processes in polymeric fluids. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1996). [Google Scholar]
- R.G. Owens and T.N. Phillips, Computational rheology. Imperial College Press, London (2002). [Google Scholar]
- M. Picasso and J. Rappaz, Existence, a priori and a posteriori error estimates for a nonlinear three-field problem arising from Oldroyd-B viscoelastic flows. ESAIM: M2AN 35 (2001) 879–897. [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- A. Quarteroni and A. Valli, Numerical Approximation of Partial Differential Equations. Number 23 in Springer Series in Computational Mathematics. Springer-Verlag (1991). [Google Scholar]
- M. Renardy, Existence of slow steady flows of viscoelastic fluids of integral type. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 68 (1988) T40–T44. [Google Scholar]
- M. Renardy, An existence theorem for model equations resulting from kinetic theories of polymer solutions. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 22 (1991) 313–327. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- D. Revuz and M. Yor, Continuous martingales and Brownian motion, of Grundlehren der Mathematischen Wissenschaften [Fundamental Principles of Mathematical Sciences]. 293 Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1994). [Google Scholar]
- D. Sandri, Analyse d'une formulation à trois champs du problème de Stokes. RAIRO Modél. Math. Anal. Numér. 27 (1993) 817–841. [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- D. Sandri, Finite element approximation of viscoelastic fluid flow: existence of approximate solutions and error bounds. Continuous approximation of the stress. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31 (1994) 362–377. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- P.E. Sobolevskiĭ, Coerciveness inequalities for abstract parabolic equations. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 157 (1964) 52–55. [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- R. Verfürth, A posteriori error estimators for the Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 55 (1989) 309–325. [CrossRef] [MathSciNet] [Google Scholar]
- T. von Petersdorff and Ch. Schwab, Numerical solution of parabolic equations in high dimensions. ESAIM: M2AN 38 (2004) 93–127. [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- H. Zhang and P. Zhang, Local existence for the FENE-Dumbbells model of polymeric liquids. Arch. Ration. Mech. An. 181 (2006) 373–400. [Google Scholar]
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


